Veterinary Endodontic Therapy
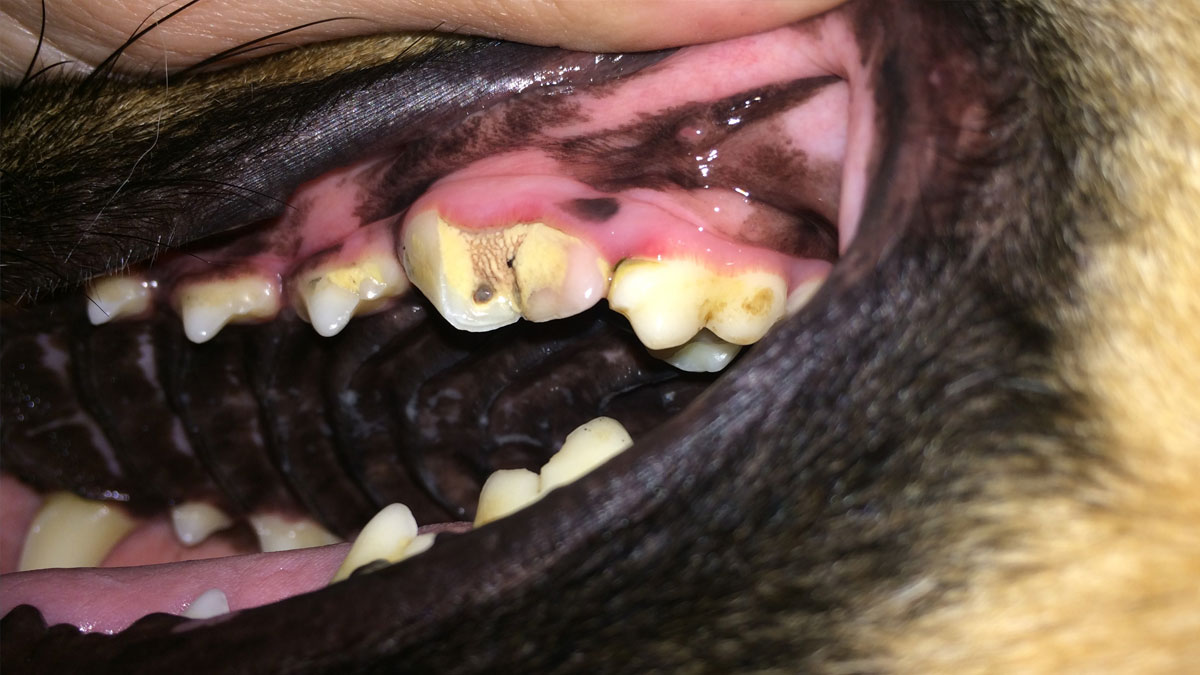
Fractured teeth are a common injury for animals. They can occur secondary to trauma, but most broken teeth result from chewing on hard objects or toys. Things such as Nylabones, bully sticks, hooves, and bones can be very damaging to dental tissue. When a tooth breaks, it needs treatment immediately. Even if the pulp is not overtly exposed, the tissue underneath the enamel, which is called dentin, will be exposed, and since there are nerves in this tissue, the tooth is painful and the pulp can easily become infected. When the pulp is exposed, however, the pain is more intense. Surprisingly, most pets will show absolutely no signs of this discomfort, even though live nerves are exposed. Left untreated, the pulp becomes infected, which causes more pain, and eventually the tooth will abscess. At this point, the bone around the tooth can also become involved, and aside from additional pain, the bone can be destroyed. A fresh fracture (less than 48 hours old) can be treated with vital pulp therapy, which allows us to keep the tooth alive and allow it to continue developing. Beyond this time frame, however, root canal therapy will be indicated. While this type of treatment will leave a non-vital tooth, it does allow the pet to keep the tooth, which aids function and cosmetics.
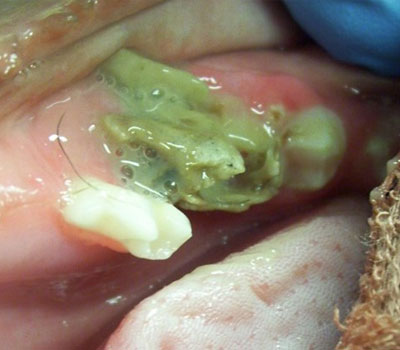
This is a graphic example of osteomyelitis, or infection within the bone, which can occur as a result of a fractured tooth. This is an extremely painful complication of not treating dental fractures.
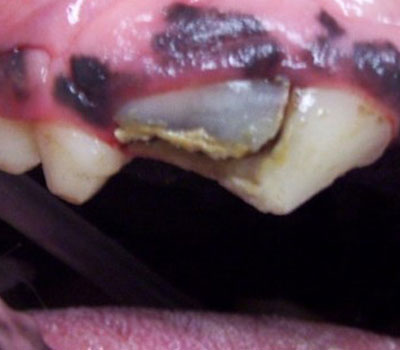
Slab fractures of the upper premolars are very common injuries, as these teeth are primarily used for chewing behaviors.
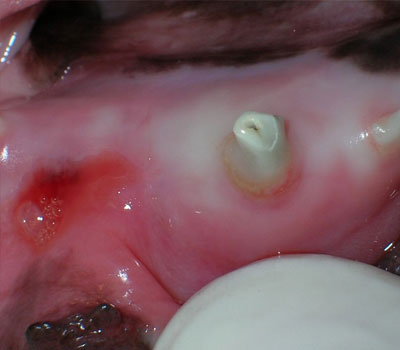
A fractured deciduous (primary, baby) can lead to an abscess that drains at a spot near the apex, or bottom, of the root.
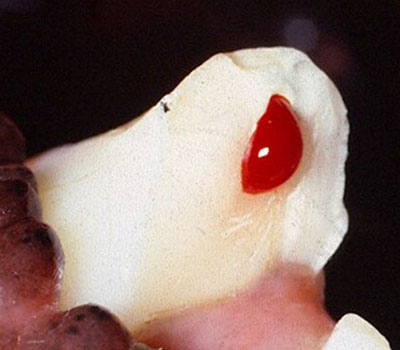
The pulp, which is the tissue inside the tooth, has a very rich blood and nerve supply, and is not immune to bleeding and pain when injured.
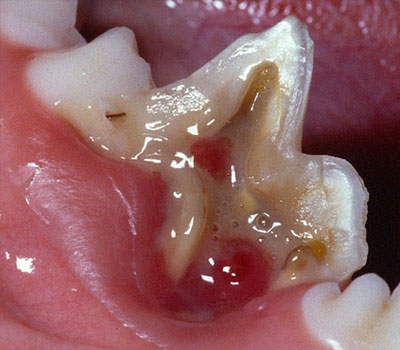
Another graphic example of the consequences that come from not treating dental fractures. This tooth is extremely infected, as are the tissues surrounding it, which are very inflamed. Dental x-rays will show that there is likely to be an abscess in the root and extensive bone destruction beneath the gums.

